Creating a CRUD API in.NET Core 9 is straightforward and allows you to build robust, scalable web services.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create, read, update, delete items, and how to use Entity Framework Core to interact with a database.
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have the following installed on your system:
- .NET Core SDK 9
- Visual Studio IDE
- Basic knowledge of C# and RESTful APIs
Create a New Project
- Open your visual studio and click on Create a new Project
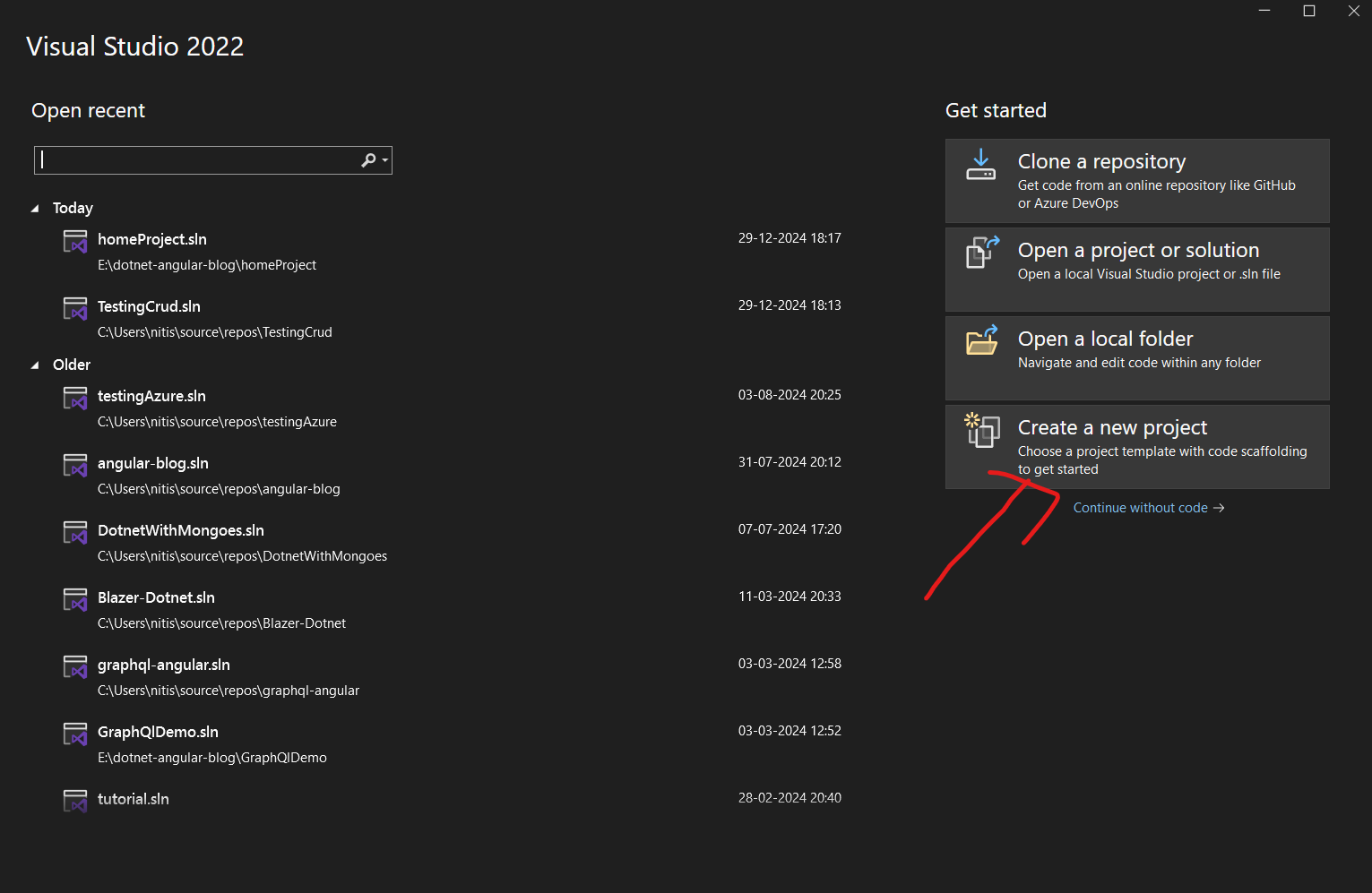
2. Select project APS.NET Core Web API, and after selecting, click on next button
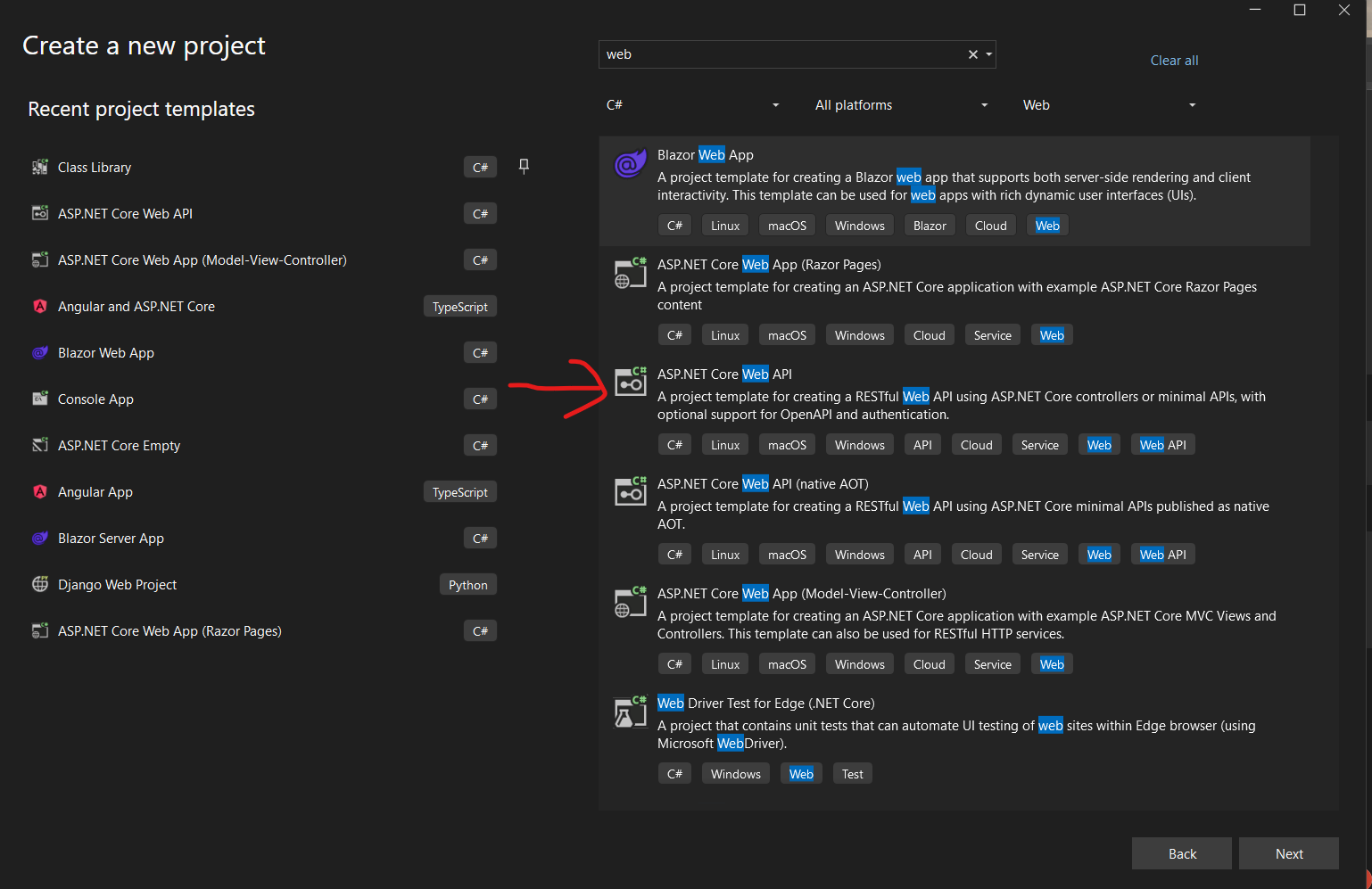
3. Enter project and click on next.
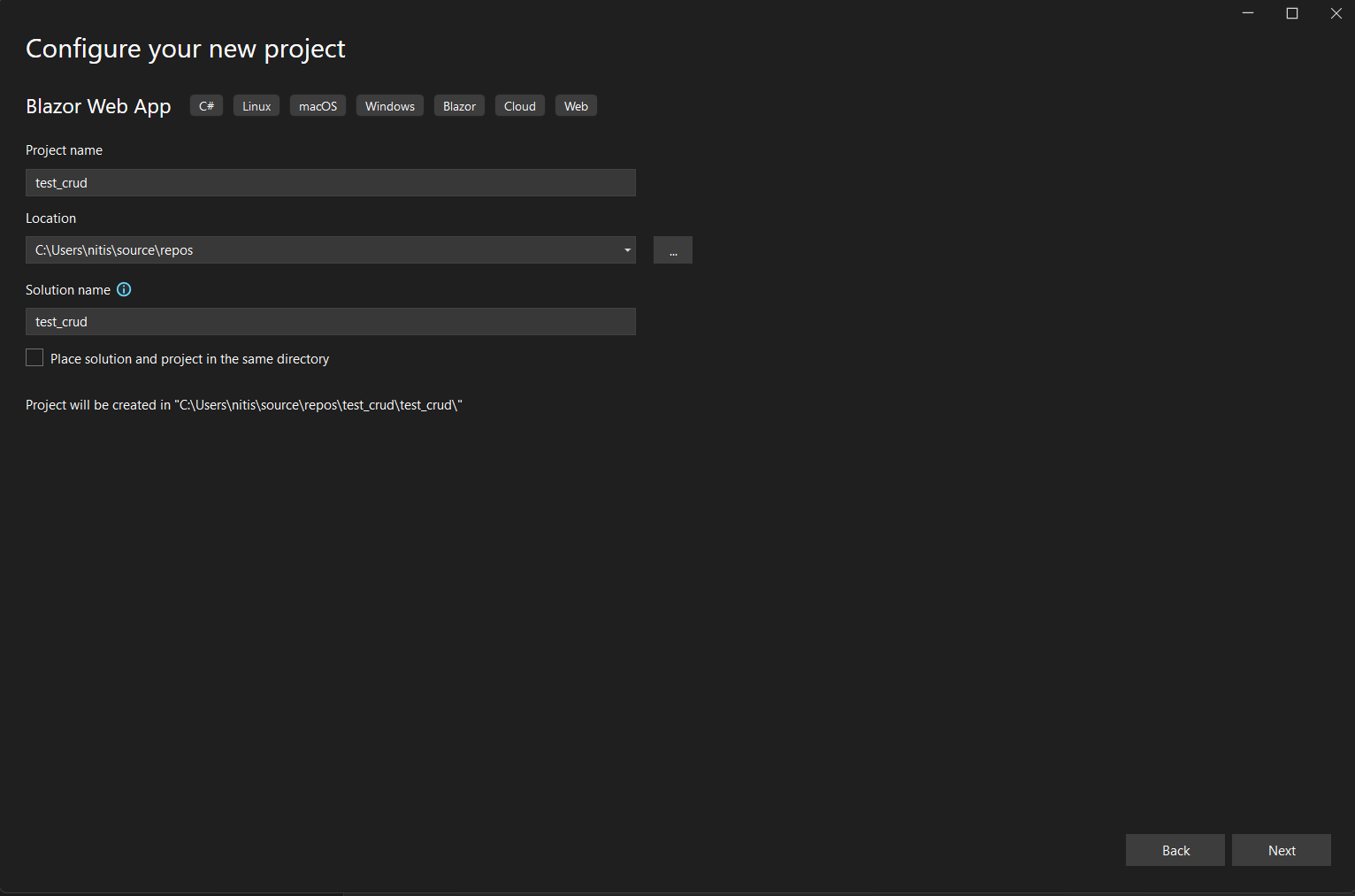
4. Select your framework and click on Create.
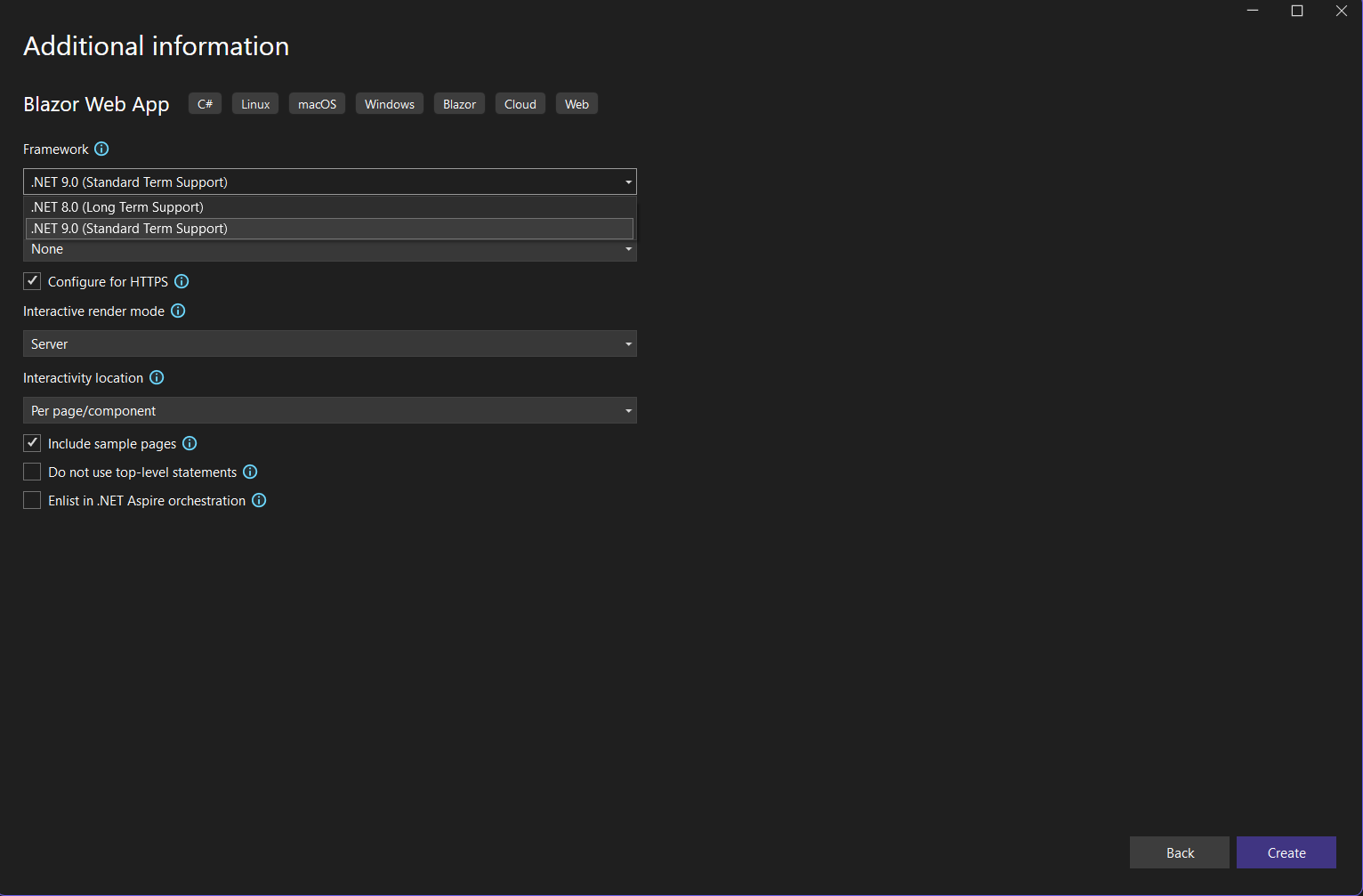
Install Entity Framework core (EF Core) and Other packages
Entity Framework Core (EF Core) is an open-source object-relational mapping (ORM) framework developed by Microsoft. It is a lightweight and cross-platform version of Entity Framework (EF).
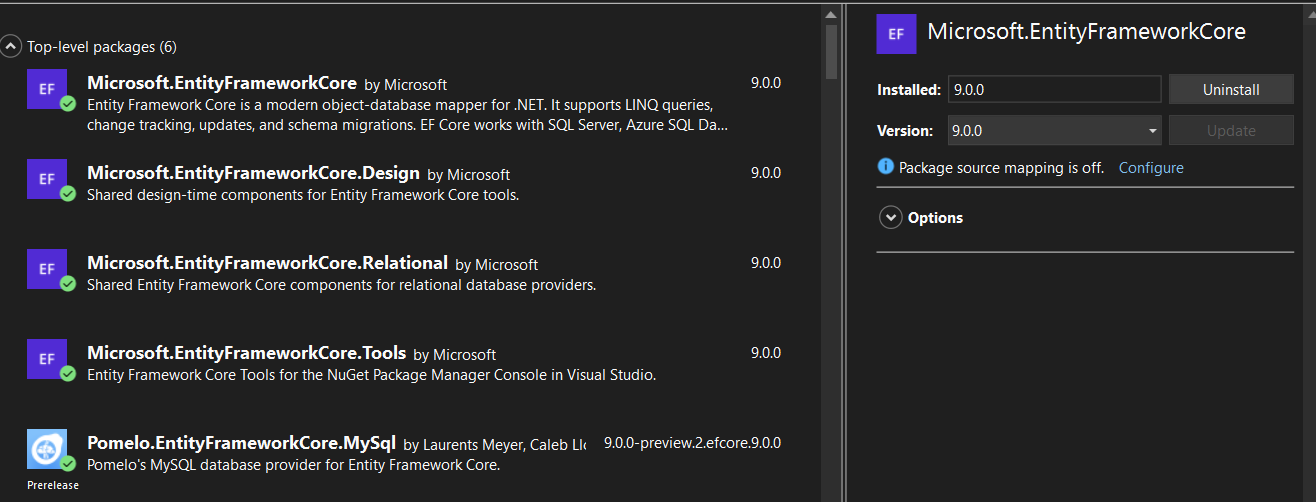
Installed the following packages.
-
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore
This is the core package of Entity Framework Core (EF Core), a popular Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework developed by Microsoft. EF Core allows developers to work with database using.NET objects,
2. Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design
The Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design packages is a companion to Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore and provides design-time tolls for Entity Framework Core (EF Core). It is used to support development tasks such as managing migrations, reverse engineering database schemas, and scaffolding code.
3. Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Relational
The Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Relational packages is a foundational library in Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore provides functionality specifically for relational datanases.It serves as a base for database providers such as SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL, and SQList. This packages is not typically added explicitly to projects, as it is included transitively when using a relational database provider.
4. Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
The Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools packages provides design-time utilities for Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore, specifically for use with the .NET command-line tool or the Package Manager Console in Visual Studio. It helps with managing migrations, scaffolding, and database updates.
5. Pomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySql
The Pomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySql Packages is an Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore provider for working with MySQL and MariaDB database. It enables EF core to interact with MySQL/MariaDB database by translating LINQ queries into MySQL-compatible SQL commands and mapping C# entities to MySQL tables.
Create The Model
Let's create a model for our API. For this example, we'll use a Employee entity
- Add a Models folder
- Create an Employee.cs file under the Models folder:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace TestingCrud.Model
{
public class Employee
{
[Key]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
[Required]
public string LastName { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Designation { get; set; }
[Required]
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
[Required]
public decimal Salary { get; set; }
[Required]
public DateTime DateOfJoining { get; set; }
public DateTime? CreatedAt { get; set; } = DateTime.Now;
public DateTime? UpdatedAt { get; set; }
}
}
Set Up the Database Context
-
Create a Data folder and add ApplicationDbContext.cs.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using TestingCrud.Model;
namespace TestingCrud.Data
{
public class ApplicationDbContext:DbContext
{
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options):base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
}
}
2. Register the database context in Program.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System;
using TestingCrud.Data;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options =>
options.UseMySql(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"), new MySqlServerVersion(new Version(10,4,25))));
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
3. Add a connection string to appsettings.json.
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "server=localhost;database=test_crud;user=root;password=;port=3306;Persist Security Info=False"
}
}
4. Open the package manager console and run migrations to set up the database.
PM> add-migration addEmployeeToDb //addEmployeeb is migration name; you can add anything migration name
PM> update-database
Create the Controller
Add a Controllers folder and create a EmployeeController.cs file.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using TestingCrud.Data;
using TestingCrud.Model;
namespace TestingCrud.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class EmployeeController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ApplicationDbContext _context;
public EmployeeController(ApplicationDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
[HttpPost("add")]
public async Task<ActionResult> AddEmployee(Employee model)
{
try
{
var employee = await _context.Employees.AddAsync(model);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return Ok(new { Message = "Employee added successfully.", data = model });
}
catch (Exception ex) {
return BadRequest(ex.Message);
}
}
[HttpGet("list")]
public async Task<ActionResult> EmployeeList()
{
try
{
var employeeList = await _context.Employees.ToListAsync();
return Ok(employeeList);
} catch (Exception ex)
{
return BadRequest(ex.Message);
}
}
[HttpGet("{id:int}")]
public async Task<ActionResult> GetEmployee(int id)
{
try
{
if(id == null || id == 0)
{
return BadRequest(new { Message = "Employee id is required." });
}
var employee = await _context.Employees.FirstOrDefaultAsync(x => x.Id == id);
if(employee == null)
{
return NotFound(new {Message = $"Employee with {id} not found." });
}
return Ok(employee);
}catch(Exception ex)
{
return BadRequest(ex.Message);
}
}
[HttpPut("update/{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult> UpdateEmployee(int id, Employee model)
{
try
{
var employee = await _context.Employees.FindAsync(id);
if (employee == null)
{
return NotFound(new { Message = "Employee not found." });
}
employee.FirstName = model.FirstName;
employee.Designation = model.Designation;
employee.DateOfJoining = model.DateOfJoining;
employee.Salary = model.Salary;
employee.DateOfBirth = model.DateOfBirth;
employee.UpdatedAt = DateTime.Now;
_context.Employees.Update(employee);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return Ok(new { Message = "Employee updated successfully.", data = employee });
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return BadRequest(ex.Message);
}
}
[HttpDelete("delete/{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult> DeleteEmployee(int id)
{
try
{
var employee = await _context.Employees.FindAsync(id);
if (employee == null)
{
return NotFound(new { Message = "Employee not found." });
}
_context.Employees.Remove(employee);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return Ok(new { Message = "Employee deleted successfully." });
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return BadRequest(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
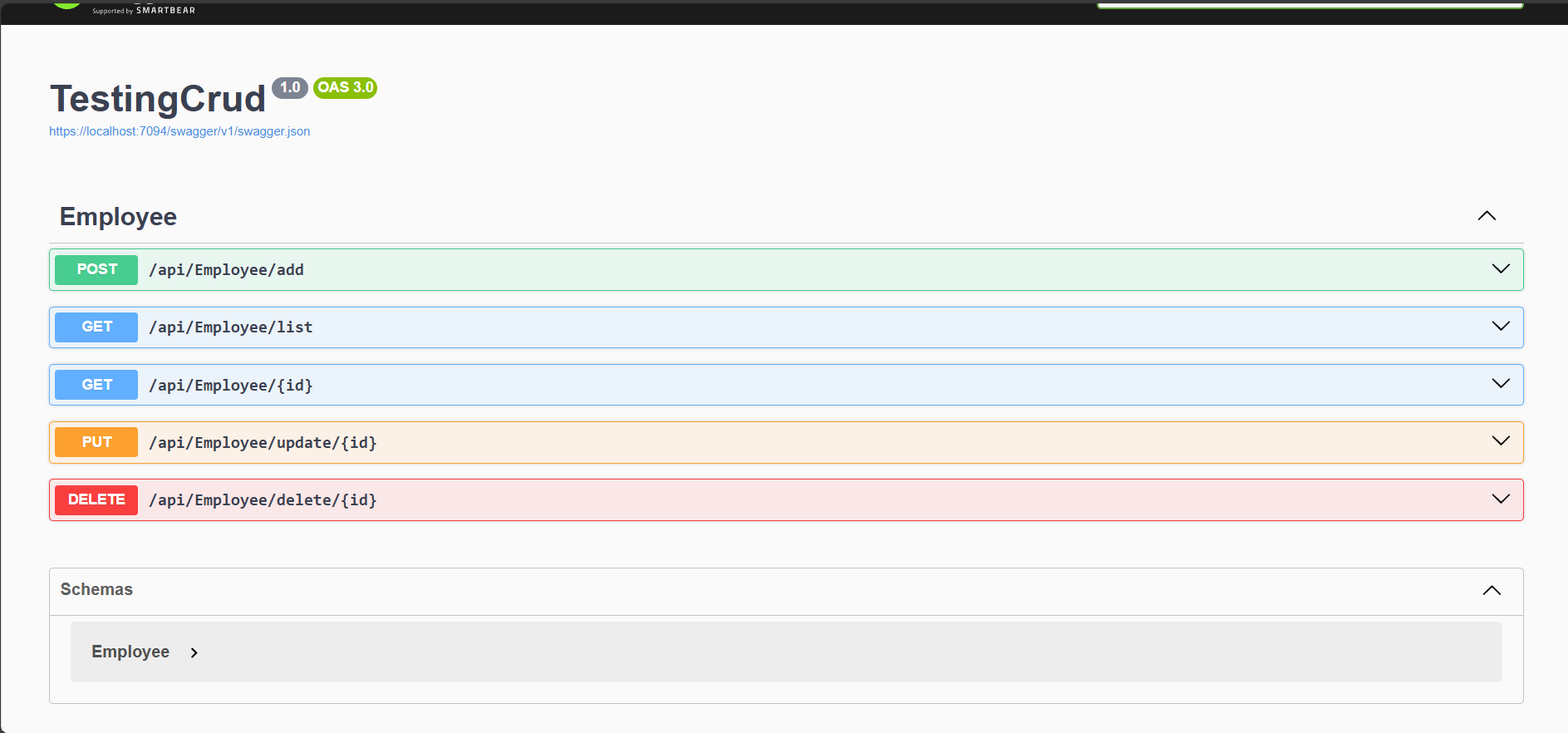
Use Swagger UI at https://localhost:5001/swagger to test the endpoints.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve created a CRUD API using .NET Core 9. This API allows you to perform basic operations on a Employee entity. From here, you can extend the API by adding authentication, validation, or more complex relationships between models.
If you have any questions or concerns, please feel free to let us know. Our team will connect with you shortly to assist.




Login to leave a comment.