Angular's Reactive Forms module provides a powerful way to build such forms, with features like dynamic validation, efficient data binding, and flexibility. This blog will guide you through creating a dynamic form using reactive forms in Angular.
Why use reactive forms?
Reactive forms provides:
- Strong control over form state: Using FormGroup, FormControl, and FormArray.
- Dynamic behavior: Add or remove form fields at runtime.
- Validation flexibility: Apply dynamic validation rules.
- TypeScript support: Makes development easier and more robust.
Create a new project
First, check you have Angular installed; if not installed, then run the command:
npm installed -g @angular/cli
Create a new angular project:
ng new dynamic-forms
cd dynamic-forms
Creating a Dynamic Form
Step 1. Setup the Component
Generate a new component:
ng generate component form
Step 2. Add ReactiveFormsModule
Import ReactiveFormsModule in app.module.ts.
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import {ReactiveFormsModule} from '@angular/forms';
import { FormComponent } from './form/form.component';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
const routes:Routes = [
{
path:'form', component:FormComponent
}
]
@NgModule({
imports: [ BrowserModule, FormsModule, ReactiveFormsModule, RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
declarations: [ AppComponent,FormComponent ],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ],
providers: []
})
export class AppModule { }
Step 3. Add forms code in forms.component.ts
import { Component, inject, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormArray, FormBuilder, FormGroup } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'app-form',
templateUrl: './form.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./form.component.css'],
})
export class FormComponent implements OnInit {
form$: FormGroup;
constructor(private fb:FormBuilder ) {
this.form();
}
ngOnInit() {}
form() {
this.form$ = this.fb.group({
name: [''],
email: [''],
addresses: this.fb.array([]),
});
}
get address(): FormArray {
return this.form$.get('addresses') as FormArray;
}
addAddress(): void {
const addressGroup = this.fb.group({
street: [''],
city: [''],
zip: [''],
});
this.address.push(addressGroup);
}
removeAddress(index: number): void {
this.address.removeAt(index);
}
onSubmit(): void {
console.log('form value', this.form$.value);
}
}
Step 4. Create the HTML template
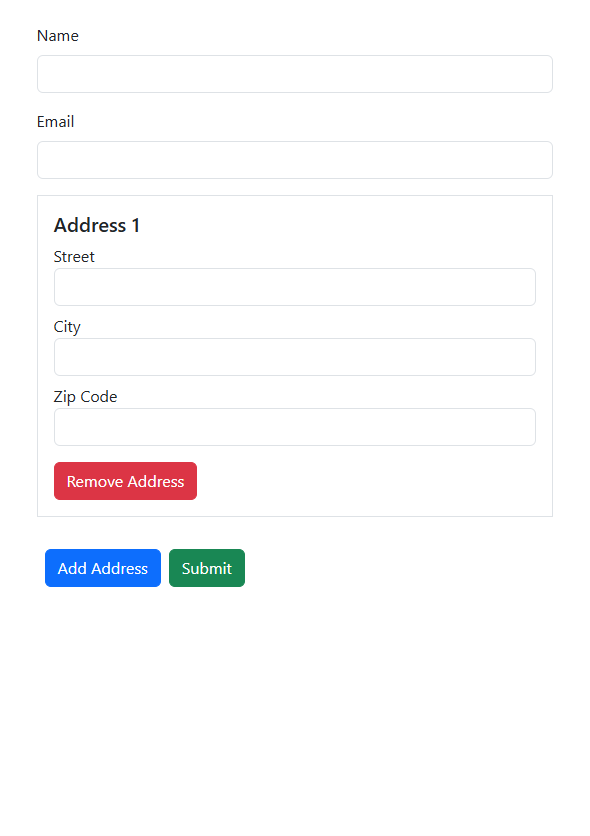
<div class="container mt-4">
<form [formGroup]="form$" (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()">
<div class="mb-3">
<label class="form-label">Name</label>
<input type="text" formControlName="name" class="form-control" />
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label class="form-label">Email</label>
<input type="email" formControlName="email" class="form-control" />
</div>
<div formArrayName="addresses">
<div *ngFor="let address of address.controls; let i= index" [formGroupName]="i" class="mb-3 border p-3">
<h5>Address {{i + 1}}</h5>
<div class="mb-2">
<label>Street</label>
<input type="text" formControlName="street" class="form-control" />
</div>
<div class="mb-2">
<label>City</label>
<input type="text" formControlName="city" class="form-control" />
</div>
<div class="mb-2">
<label>Zip Code</label>
<input type="text" formControlName="zip" class="form-control" />
</div>
<button type="button" (click)="removeAddress(i)" class="btn btn-danger mt-2">
Remove Address
</button>
</div>
</div>
<button type="button" (click)="addAddress()" class="btn btn-primary mt-3 mx-2">
Add Address
</button>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-success mt-3" [disabled]="form$.invalid">
Submit
</button>
</form>
</div>
Conclusion:
Dynamic forms in Angular provide a robust solution for creating flexible and scalable forms. By leveraging Reactive Forms, you gain precise control over the form's behavior and structure.
If you have any questions or concerns, please feel free to let us know. Our team will connect with you shortly to assist.




Login to leave a comment.